Library News
Booth Library Now Offers Free Online Access to the New York Times
Posted on December 11th, 2023
EIU students, faculty, and staff now have free online access to the New York Times through Booth Library! We are thrilled to offer this new service to better serve our students and the EIU Community as a whole.
The complimentary subscription is available to anyone with an eiu.edu email address- including retired employees and emeritus members!
Online access to the New York Times through EIU Library includes:
- 24/7 Breaking News
- Archives (dating back to 1851) timesmachine.nytimes.com/browser
- Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality – found in the App; NYT stories told through enhanced technology
- Daily 360 content – two dimensional, 360° views (with mobile device or using a mouse)
- Podcasts (including The “Daily” podcast)
- All multimedia, including video, photography, VR features, and new multimedia to come.
- Newsletters (there are a variety of topics that you may subscribe to)
- Spanish and Mandarin Chinese versions of NYTimes.com.
Activate your access to The New York Times, compliments of Booth Library here.

Booth Library will host NEA Big Read: Reconsidering the American Dream
Posted on November 10th, 2023
Booth Library at Eastern Illinois University is once again hosting the National Endowment for the Arts Big Read. The theme, Reconsidering the American Dream, will be explored by reading and discussing two books: Heartland: A Memoir of Working Hard and Being Broke in the Richest Country on Earth by Sarah Smarsh, and Infinite Country by Patricia Engel. A limited number of free copies of the books are available at Booth Library. Discussion groups will be organized and plan to meet in January, February and March. Dates and details will be provided to participants in early January. Additionally, look for announcements of statewide public programs sponsored by Illinois Humanities. Further information about the Big Read can be found on the Illinois Humanities website.
- In support of The Big Read from the National Endowment from the Arts and Arts Midwest, LAB students will team with librarian David Bell to host a student led book club this spring. The theme, “Reconsidering the American Dream,” will be explored through the novel Infinite Country and the memoir Heartland: A Memoir of Working Hard and Being Broke in the Richest Country on Earth. Both books are available for checkout at Booth Library. Join members of the LAB at the following times:
- Thursday, February 1 from 6 p.m. – 7 p.m. for a kick-off book talk event to learn more about the titles, discussion groups and how to get a copy
- Thursday, February 29 from 6 p.m. – 7 p.m. for book discussion in Edgar Reading Room
- Thursday, March 28 from 6 p.m. – 7 p.m. for book discussion in Edgar Reading Room
- All events are open to students, faculty and staff. Questions? Contact David at dsbell@eiu.edu for more info
NEA Big Read is a program of the National Endowment for the Arts in partnership with Arts Midwest.

‘A picture is worth a thousand words’
Posted on March 24th, 2023

By Madeline Steiner
University Archives Intern
Among the University Archives at Booth Library are numerous collections of historical documents, objects, and photos – items that carry so much historical information and significance. One such collection is that of Eastern’s all-class photographs, “all-class” meaning everyone involved in the school, including professors, students freshman through senior, and, in most cases, the lab school students, as well.
Today, it sounds like a pretty daunting task just to get one whole class into the same photo, let alone the entire school; however, the collection is a small one, including six panoramic photographs from the late 1910s into the early 1920s, when the class sizes were much smaller. Eastern opened its doors to students on Sept. 12, 1899, with a starting faculty of 18 and with around 125 students. As the years went on, the numbers grew and were up to around 450 in the 1919 school year and in 1924, students, faculty, and lab school students made equaled about 600, which was still rather manageable for a photograph.
Item #1 in the collection is not dated but is from around the late 1910s into the early 1920s, notable by the fact that the school is still titled Eastern Illinois State Normal School, which was Eastern’s name upon being approved in 1895. The name then changed in 1921 to Eastern Illinois State Teachers College. This change can be noted through the timeline created by the photos.
Item #4 was taken March 31, 1921, near the end of the school’s time as Eastern Illinois State Normal School. Item #3 was taken Dec. 8, 1921, and is titled Eastern Illinois State Teachers College. The name change was made between March and December in 1921. Item #4 is also not dated on the physical photograph but can be found in the school’s 1921 edition of the Warbler (they used to print fairly detailed schedules of the entire year in the Warbler), which also includes numerous photos of classes, faculty, and campus.
Of the six photographs, five were taken by Kansas City, Missouri photographer Verne O. Williams, who was evidently well-versed in panoramic photographs. His 1917 Camp Funston series is proof of this. The seven panoramic style photos document the year of construction on Fort Riley’s Camp Funston in Kansas, including construction progress of the entire camp, staff members, and even the crowds of the 1917 football game against the University of Illinois.
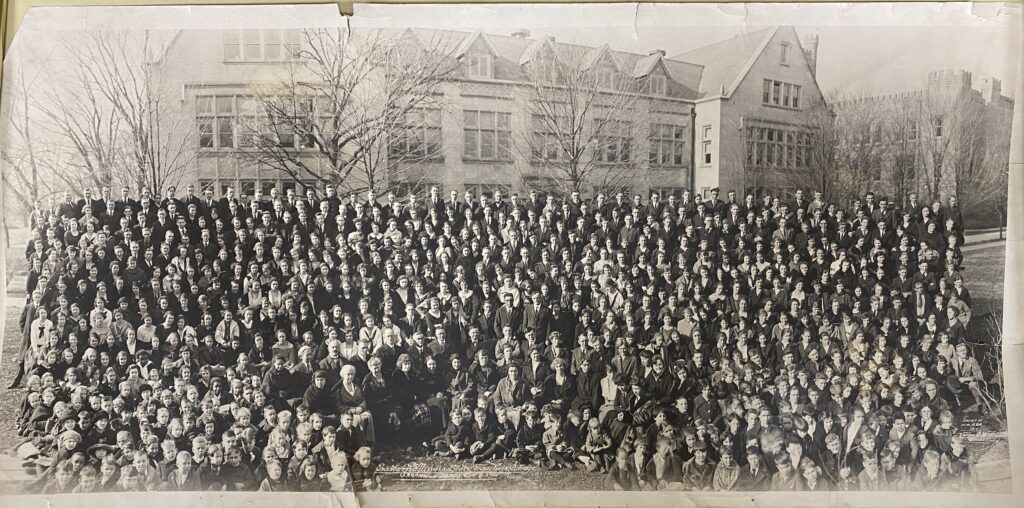

The panoramic photo was quick to be experimented with upon the invention of the camera in 1839. Early panoramas were produced by placing two or more daguerreotype panels (the first commercialized photographic process) next to each other and they began appearing as early as 1851. Because of the desire for panoramic photos, in the late 19th century, cameras were mass produced specifically for panoramas.
The first mass-produced American panoramic camera was in 1898. These mass-produced cameras were easy to develop but could only create small panoramas that could be no longer than 12 inches and only had a field of vision of about 180 degrees, so, in 1904, the Cirkut Camera was patented. This panoramic camera was capable of producing a 360 degree photograph measuring up to 20 feet long. We can infer from the Eastern Illinois prints that Williams might have used a Cirkut Camera because these cameras were commonly used for group photographs and landscapes. Plus, every photo in the collection is well over 12 inches long, with the shortest in length being 32 inches and the longest at 46 inches.
Studying these photos could easily lead the researcher down a rabbit hole of information about Eastern’s past. For example, most of us probably know that Pemberton is one of the oldest buildings on campus, but the greenhouse seen in one of the collection’s photos was the second oldest structure, next to Old Main. Built in 1902, it was designed to provide decorative greenery for the main building. This greenhouse can be seen in the oldest of the collection’s photos, which was taken behind Old Main, in just about the middle of what would be the North Quad today.
Pemberton, only barely noticeable in the same photo, was the third building approved in 1907 and named after Senator and Eastern supporter Stanton C. Pemberton in 1909. Built as an all-female dorm, it was Illinois’s first college dormitory built for the purpose of creating a real campus community. Lord “wanted it to be more than a boarding house; he wanted to provide a family atmosphere for the students” (Otta, 58). Because it was the first of its kind in Illinois, it took a lot of work on the part of President Lord and Senator Pemberton, but it was finally approved, along with a “cracker box” gymnasium, in 1907 and was formally opened in January of 1909.
Blair Hall, seen behind students and faculty in photograph #3, was the fourth building on campus. Blair, originally named the Training School Building, was built for the purpose of training future teachers through the Model School, which was moved there upon the building’s completion in 1913. Later it was referred to as the “lab” school, and was attended by the children of Charleston as well as university faculty. The Training School Building was renamed Blair Hall in 1958.
The details of history can be found anywhere if you look hard enough and do the research. The 1920s all-class photo collection is just one example of many that packs so much information into a few images.
Madeline Steiner is a senior majoring in English from Lincoln, Illinois.
Works Cited
“Barnhart, Terry. “That ‘Noble Project:’ The Founding of Eastern Illinois University and the Origins of Old Main, 1895-1899.” Eastern Illinois University, https://www.eiu.edu/localite/oldmainnobleproject.php. Accessed 24 Feb. 2023.
“A Brief History of Panoramic Photography.” Library of Congress, https://www.loc.gov/collections/panoramic-photographs/articles-and-essays/a-brief-history-of-panoramic-photography/. Accessed 3 Mar. 2023.
Eastern Illinois University, “1918-1968 Warbler: ‘On the Road to Somewhere,’” 1968. The Warbler, 2. http://thekeep.eiu.edu/warbler/2.
Otta Sherri, “Still Going Strong,” 1990. The Warbler, 63, p58-59. http://thekeep.eiu.edu/warbler/6.
Williams, Verne O. and Charles A. Stead. Camp Funston, Fort Riley, Kansas. 25 Jul. 1917, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/archives/218831.
—. Camp Funston, Fort Riley, Kansas. 29 Aug. 1917, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/archives/218834.
—. Camp Funston, Fort Riley, Kansas. 19 Sep. 1917, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/archives/218840.
—. Camp Funston, 14th National Army Cantonment, Fort Riley, Kansas. 1917, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/archives/226933.
—. Engineers, Sanitary Train, Fort Riley, Kansas. 28 Sep. 1917, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/archives/226891.
—. Field Auditor’s Staff, 14th National Cantonment, Camp Funston, Fort Riley, Kansas. 3 Oct. 1917, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/archives/226887.
—. Football Crowd at Camp Funston, Fort Riley, Kansas, Thanksgiving Day. 29 Nov. 1917, Kansas Historical Society, https://www.kshs.org/archives/226921.
Study success kits available on 4th floor
Posted on March 3rd, 2023
A study session goes much better when you are relaxed, focused, and feeling good about yourself. Booth Study Success kits have items to help students get in the right frame of mind to do their best work.
Affirmation cards give you scripts for positive self-talk. Fidget toys can help burn off anxious energy. Timers offer a soothing visual experience and a way to time a break in your study session.

Do fluorescent lights or screen glare leave you feeling overwhelmed? Block the blue light wavelength with the blue-blocking glasses in the kit. If it’s the noise rather than the light that is a distraction, we also offer ear muffs, ear plugs, and a white noise machine.
Feeling ungrounded and floaty? Borrow the weighted blanket for some calming coziness.
All items are available at the Library Technology Services counter on the fourth floor. Kits are available for checkout for one day. The earmuffs, sound machine and blanket must be used in the library. The ear plugs are yours to keep.
Teams invited to break the code at Booth!
Posted on January 9th, 2023
Can you break your code before the other teams? Assemble your team of up to four students to compete in Booth Library’s CodeBreakers at 5 p.m. on Jan 25.
Your team will be in a race against the clock, and seven other teams, to decipher your code phrase. Teams will follow clues that lead them throughout the library. The fastest team to crack their code will win the grand prize!
This experience is limited to the first eight teams to sign up. Register your team here.

Stream music for free on Naxos
Posted on December 9th, 2022
Naxos Music Library is a streaming platform accessible through Booth Library’s website. On the homepage, click “Databases,” and it’s sorted alphabetically.
Naxos lets you listen to classical music in many categories: opera, ballet, instrumental, vocal, jazz, and more! Now, you can’t find the new Harry Styles or Taylor Swift albums in this resource, but there are many other choices of music that can be good for many things such as listening to instrumental music while studying, choreographing a dance, practicing vocals, or maybe you’re not into the music that plays on the radio today and you’re looking for something different.
You can create playlists, sort by genres, and more! It’s worth exploring to see if there’s any way this resource can be helpful for your educational or personal use. Follow these links to access:
The future of postcards
Posted on November 28th, 2022
The EIU Archives has a catalogue of thousands of old and new postcards from around Illinois, the United States, and the world that can provide insight into history, art, and culture not seen elsewhere. You can access many of them through the Booth Library online database, but to see the complete collection, one must come to the Archives in person.
By: Chloe S. Guiliani, EIU English major and senior
The 150th anniversary of American-made postcards is coming up on May 13, 2023, but the Golden Age of postcards are long behind us, ending over 100 years ago in 1915. Over the decades since, postcards have slowly fallen out as a popular form of correspondence. [1][2]
According to a 2017 article by Jeanette Settembre on the Market Watch website, with the rise of the Millennial generation and continued technological advancements, postcards have been cast to the wayside in favor of more convenient, instant communication. Historic postcard-publishing companies are shuttering, if they haven’t already; England’s oldest postcard publisher, J Salmon, halted their printing in 2017 and sold what remained of their stockpile throughout 2018. “Just 25 years ago more than 20 million postcards were sold each year, but now the number has dipped down to just five or six million.” [3]
With the prevalence of social media and reduction in the deliveries of physical mail that people receive each day, people today do not need to rely on postcards to communicate quickly or to capture vistas. Instead, we can easily take our own pictures and selfies on our mobile devices and choose whether to post them online, send them via text or email, or print them out. We can even edit and design our photos to look like a classic postcard, if we wish.
Plugging the term “postcard” into Google Trends will present you with the following graph, which seems to mark the slow downfall of the postcard in the digital age. According to Google Trends, which can track internet search terms from January 2004 to the present, the term “postcard,” to this day, has never reached the peak level of American web searches as it did in February 2004, with an interest value of 100. Currently, in November 2022, the interest value of “postcard” is only 24, which means that American searches for that term are down by 76% from its peak figure nearly 19 years ago. The interest value numbers look even worse for postcards when taking the Google Trends search worldwide, where the peak value of 100 was in December 2004 and is now only 5.
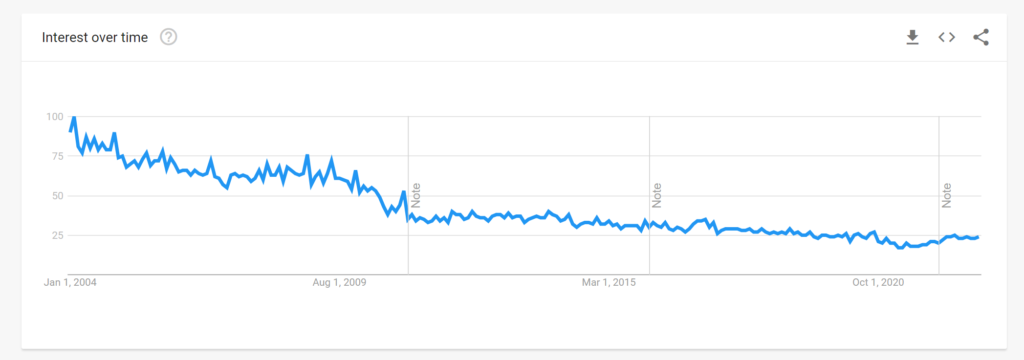
What then, does the future of the postcard look like outside the museum or archives? Do you remember the last time you received a postcard in the mail?
As a business, things don’t look bright, but the interpersonal exchange of pictures and short correspondence has not stopped. Looking to American-focused Google Trends again, it took only one year after the initial launch of the Facebook program in February 2004 for it to be searched for online more than postcards; the exact same can be said for Instagram, launched in October 2010.
Texting through SMS and MMS messaging has also exploded on the mobile market. In 2022, research points to 18.7 billion SMS and MMS messages being sent worldwide each and every day, which is a 7,700% increase in the number of texts sent over the past ten years. [5]
While the quick exchange of images and information will continue to grow and evolve, postcards as a medium to do so seem to slowly be going extinct, and if that is so, it will take archivists, researchers, historians, and collectors to preserve them as a flashpoint in the history of written communications.
Author’s Note: Chloe S. Guiliani is completing an internship this semester in the Booth Library University Archives and Special Collections.
Works Cited
- A History of Postcards. (n.d.). Seneca County, New York – The County Between the Lakes. https://www.co.seneca.ny.us/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/Postcards-History-ADA.pdf
- Kentic, J. (n.d.). How Many Texts Are Sent Per Day? Modern Gentlemen. https://moderngentlemen.net/how-many-texts-are-sent-per-day/
- Postcard Collection – Essay, Appendix C: Manuscripts and Special Collections: NYS Library. (n.d.). Home Page: NYS Library. https://www.nysl.nysed.gov/msscfa/qc16510ess.htm
- Postcard – Explore – Google Trends
- Settembre, J. (2017, September 30). Postcards are becoming extinct and 5 other industries millennials are killing. MarketWatch. https://www.marketwatch.com/story/postcards-are-becoming-extinct-and-5-other-industries-millennials-are-killing-2017-09-30
My favorite postcard at the EIU Archives
By: Chloe S. Guiliani, EIU English major and senior
In all of my work at the EIU Archives, I hadn’t seen night-time views or inclement weather displayed on any of the postcards to which I was assigned. The views were predominantly of the daytime, where clear and sunny skies could lend to the design by lighting certain areas and casting shadows off objects or buildings. And even when it was obvious that the postcard displayed a winter view, the snow and barren trees were always picturesque and peaceful.

When I thought back on postcards I had seen in my own travels, I couldn’t think of any that stood out for weather or lighting reasons. Idealism is usually at the forefront of postcard design, since potential buyers are more likely to want postcards that capture “the best” an area or view can offer (and not necessarily what it looks like on the average day).
What first caught my attention with this card, in particular, was that it was a night-time view, but it wasn’t what kept me engaged. It seemed so low key compared to the “look at me, look at me” nature of most postcards. At the time of discovering this card in the archival collection, I was working on a project about “Lo-Fi” art, from audio and music to visual works, and what makes something “low fidelity.” Looking at the postcard, I thought to myself, “This has to be the first and only postcard I’ve ever seen that is a Lo-Fi artwork!”
It seemed as though the essence of the postcard was a typical view one might have of the library at night while walking on the sidewalk. It’s a very warm and inviting image, and as an English major, it makes me feel like there’s more of a story here. Just as a postcard might segue a person into reminiscing on an experience, the image pictured on this postcard made me think, “What happens next? What is the story behind this setting?”
And as someone with a knack for detail, there are certain efforts I see in this postcard that I have not seen in many (if any) others. From the way the light shines realistically on the “Roanoke Public Library” sign and doesn’t encompass every letter of it with brightness; or the way the foliage blocks the direct view of the door and matches the background foliage’s lighting technique, making the library feel surrounded by greenery (and it actually is, being situated in a city park).
I was also fascinated at how such a simply designed postcard could make the foliage look so well at night and highlight the silhouette of the background’s canopy, which contrasts with the subtly shaded night sky. Not only does the slight change in tint around the trees make the border between sky and tree more clearly visible, but it gives depth to the small amount of outer space depicted, and it shows that the rest of town is lit up, too (if we could only see past the foliage).
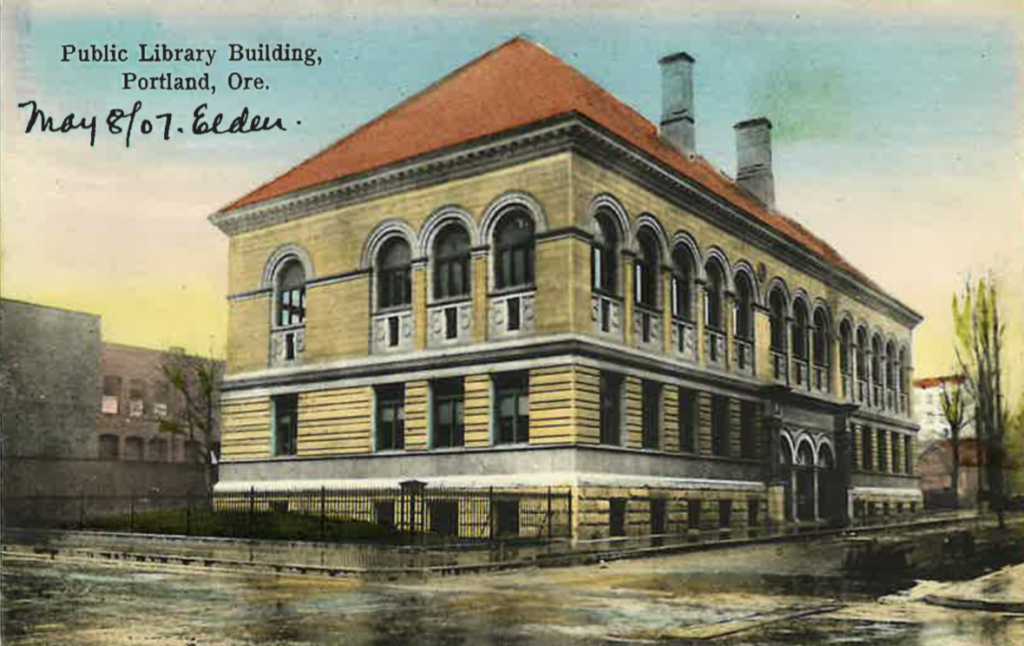

My runner-up for favorite postcard was a library view from Portland, Oregon. First, there are no other postcards that I have seen with such a watery sheen on the ground. In the design, one can also notice that the background is a rough U-shape of out-of-focus skyline, and that the actual focus of the foreground isn’t just the library building but the condition of the road in front of it. Considering the fact that Portland is a city with the third-most rain/snowfall in the entire United States, it only makes sense to not only have postcards with rain in them, but make that rain just as beautiful or omnipresent as it actually can be.
Author’s Note: Chloe S. Guiliani is completing an internship this semester in the Booth Library University Archives and Special Collections.

The craze of postcards: How they connect modern times to our shared past
By: Chloe S. Guiliani, EIU English major and senior
It may not seem that important to understand the origins of the postcard and picture-postcard, but postcards and their history not only give you an idea of what something looked like at a given time in history, but the history of human communication, the marketplace of ideas, and cultural exchange. In 1905, the Nottingham Sun was quoted in their report that postcards were “strengthening the bonds of international as well as individual friendship.”

They originated in the mid-to late 1800s, the time where the world was opening up due to the industrial revolution, and so, for the first time, people were able to send and receive messages and pictures from around the planet for as low as half the price of mailing letters in an envelope. For the people of that time, postcards acted like our modern texting, whereas letters would represent a phone call.
In fact, it was the opinion of many in that time that postcards would “ruin society,” whether they had pictures on them or not, just as we hear today about the linguistic effects — good or bad — that could come from texting or internet lingo becoming so commonplace. They argued then that with the limited space on a postcard, the result would be the ruination of polite conversation.
In addition, since most postcards weren’t in an envelope, they would lead to invasions of privacy amongst the population. This is still a topic at the forefront of much of society today, especially involving the privacy-encroachment that internet connection and social media bring us.

Though the picture postcard wouldn’t become a staple or craze until around the turn of the 20th century, advertisers had been inspired in the early 1870s to use postcards as “open announcements.” They were first restricted to written announcements, but the picture-variety arrived shortly after.
Impetus for the picture postcard grew at the Paris Exhibition of 1889, where the Eiffel Tower — just recently completed — acted as a major attraction for France. There, visitors could not only go up the Eiffel Tower but buy a postcard with its printed image and post it directly from the top of the tower. This trend caught fire and started the entire “postcard craze,” which spanned around the world from Paris to Vienna and the United States to Imperial Japan.

Subsequently, postcards became a hot item, and you could buy and post at the summit of whatever tower, lighthouse, road, or big and notable hill you happened to find yourself. Postcards were a quick and cheap way for our recent ancestors to capture and share an experience, and prove they’d done or seen it, whatever it may be, just as we modern people might make a social media post of a landscape or a selfie of ourselves whenever we happen to climb a mountain, reach a scenic overlook, or make it out of the grocery store in less than 15 minutes.
It might seem odd, but even the postmark over the stamp mattered, since it proved where and when you had sent the card from exactly, and collectors wanted it to match the location pictured on the card. This mattered so much, in fact, that many folks posted their cards to themselves. Not only that, but in France, you could take cards you never actually posted into the post office just to receive that valuable postmark, if only to get that gratifying feeling and prevent postmark FOMO. These historical “social media location filters” were valuable, not only to hobbyists and collectors then but collectors and historians now.
The entry to the EIU Archives is located inside the south atrium of Booth Library, by the clock tower. The 1972 second-edition Pictures in the Post: The Story of the Picture Postcard and its Place in the History of Popular Art by Richard Carline is available for checkout at Booth Library.
Works Cited
- Carline, R. (1972) Pictures in the Post: The Story of the Picture Postcard and its Place in the History of Popular Art. 2nd Edition. Philadelphia , PA: Deltiologists of America.
Author note: Chloe S. Guiliani is completing an internship this semester in the Booth Library University Archives and Special Collections.
Booth wins Atkinson award for its digital literacy program
Posted on July 13th, 2022
Booth Library was the recipient of the Illinois Library Association’s 2022 Hugh C. Atkinson Memorial Award for Interlibrary Cooperation, which is awarded annually for sustained activity and contributions having a lasting impact on librarianship. The award is supported by the Hugh C. Atkinson Memorial Fund and by the Valerie J. Wilford Memorial Fund established in recognition of contributions to multi-type cooperation and resource sharing.
In 2021, EIU’s Booth Library was awarded a grant from the Illinois Department of Commerce and Economic Opportunity’s Illinois Broadband READY program. The library received $44,000 to create a digital literacy program for the Southeast region of Illinois. With the grant funds, a digital literacy coordinator was hired to create curricular materials related to digital literacy for all ages – from elementary school students to retirees.
With proper feedback, the digital literacy coordinator successfully created a robust curriculum that covered various digital literacy topics. Additionally, a “train-the-trainer” model was implemented along with vigorous online literacy guides. Booth Library partnered with the Charleston Carnegie Public Library, Mattoon Public Library, Effingham Public Library, and the Elizabeth Titus Memorial Library in Sullivan. Additional program partners were the Lake Land College Adult and Alternative Education program, EIU Academy of Lifelong Learning, and Mattoon Community Unit School District 1.
Chris Houchens, Director of the Charleston Carnegie Public Library wrote in his nomination letter, “Booth Library has been an excellent partner not only to us, but all of the surrounding libraries in our littler corner of Illinois. I could not think of a better Library for the Hugh C. Atkinson Memorial Award for Interlibrary Cooperation.”
The Hugh C. Atkinson Memorial Award was presented at an awards ceremony during the 2022 Illinois Library Association Annual Conference on Oct. 18-20, 2022, in Rosemont, Illinois.
Counseling and therapy streaming videos available!
Posted on May 18th, 2022

Booth Library acquired three collections from Alexander Street Press’s Counseling and Therapy in Video series of streaming videos, completing our acquisition of the full library of content (Volumes I-V).
Volume III includes films about the founders of theory and the progression of practices to today. These titles present a firm grounding in the theoretical modalities of counseling and psychotherapy while expanding into new and emerging areas such as social media, veterans, cyberbullying, mindfulness, and neuroscience.
Volume IV focuses on prevalent issues in counseling, such as the rise in cases involving underserved populations, racial trauma, and veterans suffering from PTSD. This volume delivers content aligned with the CACREP eight common core areas, and introduces the DSM-5® and ICD-10. It includes 300 hours of video, 90% created since 2012; 400 transcripts from real therapy sessions; 1,200 hours of expert-led presentations, lectures, and workshops; and 45,000 pages of ebooks and periodicals.
Volume V, the Symptom Media Collection, has comprehensive DSM-5® / ICD-10 coverage with built-in assessments to assess comprehension. Ideal for counseling, psychology, social work, nursing and other behavioral health care courses, Volume V helps students better recognize mental health disorders and provides accurate diagnoses via 400+ streaming mental health videos aligned to DSM-5®/ICD-10 content. Assessment options included.
EIU students, faculty, and staff can access these videos from both on- and off-campus. Please ask a librarian for further assistance, or consult with your subject librarian.
Library creates health literacy program
Posted on April 26th, 2022
Booth Library was awarded $18,000 from the National Library of Medicine to implement a health literacy program in the Southeastern region of Illinois.
With the award funding, Booth Library partnered with the EIU Department of Public Health and Health Communication program to create a virtual training module including videos and resources on various health literacy topics. Content was based on the needs of local public libraries and community organizations.
The grant program was led by Stacey Knight-Davis, Booth Library health and nursing librarian; Dr. Lauri DeRuiter-Willems, Department of Public Health and Nutrition; Dr. Beth Gill, School of Communication and Journalism; Kim Ross and Carrie Wennerdahl, digital health literacy coordinators.
A library guide about digital health literacy was created as a result of this program. It can be accessed at https://eiu.libguides.com/dighealthlit/.
This program was funded by Region 6 of the Network of the National Library of Medicine, whose mission is to provide U.S. researchers, health professionals, public health workforce, educators, and the public with equal access to biomedical and health information resources and data.
This work was supported by the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health, under Cooperative Agreement number UG4LM013729 with the University of Iowa. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.




